Anchors are an important part of the maritime industry and play an essential role in keeping vessels in place. Their weight is crucial to maintaining stability and preventing accidents. In this blog post, we will explore the weight of a ship anchor and how it affects the maritime industry. We will also look at some alternatives to traditional anchors that may be more environmentally friendly.
What is an Anchor?
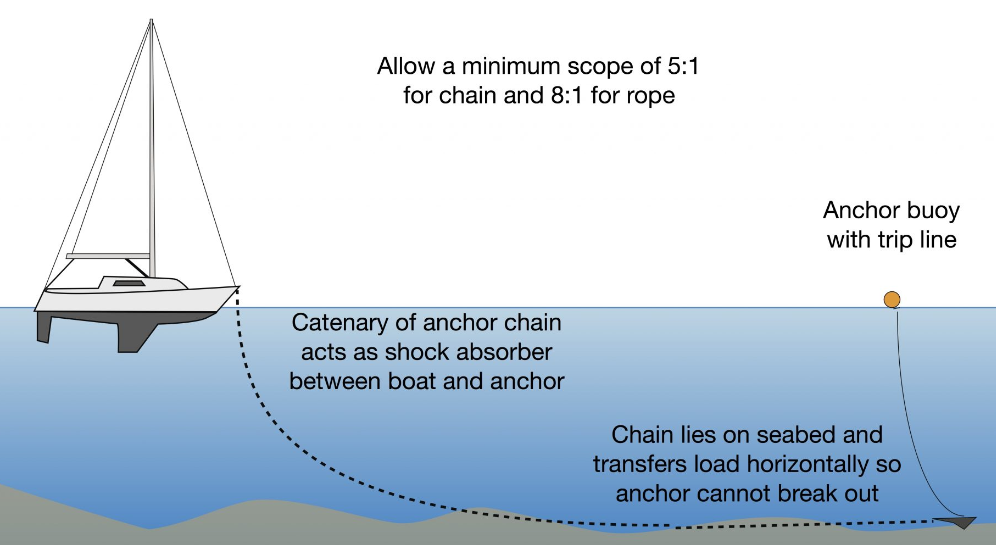
An anchor is a weight used to secure a ship to a seabed or pier. The primary purpose of an anchor is to hold the ship in place, preventing it from moving. There are several different types of anchors, each with its own specific purpose. An anchor chain is the most common type of anchor and is made up of a number of individual links. When tension is applied to the chain, it locks the ship into place. An anchor cable is similar to a chain but consists of a long, thin cable instead of individual links. When tension is applied to the cable, it also locks the ship into place.
How Much Weight Does an Anchor Weigh?
An anchor weighs anywhere from 500 to 4000 pounds, depending on its size and make. A 600-pound anchor can stop a 200-foot ship in its tracks, while a 4000-pound anchor can hold back a 6600-foot vessel.
Anchors are typically made of steel, with a lead weight at the bottom to keep it anchored in the ground.
Factors That Affect Anchor Weight
Anchor weight is a critical factor in determining how much a ship can anchor in a particular location. Anchor weight also affects the buoyancy of an anchor system, and the amount of power needed to pull the anchor from the ground.
The size and type of an anchor’s chain can significantly affect its weight. A chain with fewer links will weigh less than a chain with more links, and a chain with smaller diameter links will weigh more than a chain with larger diameter links. The weight of an anchor also depends on its material and construction. For example, steel anchors are heavier than nylon anchors, and round anchors are heavier than pointed anchors.
The dimensions of an anchorage also play a role in anchor weight. An anchorage with deeper water will have more mass per unit area than an anchorage with shallower water, which will cause the anchor to weigh more.
How Does an Anchor Work?
An anchor is a large weight attached to a cable that is used to keep a ship or boat stationary in the water. The anchor weighs several tons and can be as long as 20 feet. The anchor is usually connected to the ground by a long cable.
When the anchor is pulled up from the ground, it causes the cable to tighten. This causes the ship or boat to stop moving. If the anchor is not released, the cable will eventually break and the ship or boat will continue to move.
The Weight of an Anchor

An anchor is a weighty little piece of hardware, used to secure a ship to the ground. Anchors come in all shapes and sizes, but they all have one thing in common- they weigh a lot!
Anchors can weigh anywhere from a few ounces to more than 100 pounds. The weight of an anchor depends on the type of anchor, the material it’s made out of, and the size of the anchor.
The average weight for an 8-inch diameter steel cable anchor is about 12 pounds. For an 18-inch diameter anchor, the average weight is about 25 pounds. And for a 30-pound anchor, that’s about 50 pounds!
Anchors are generally designed to hold up to a certain amount of weight. If the anchor is overloaded, it can eventually break or fail. Overloading an anchor can cause it to drag along the seafloor, damaging ships and other objects nearby.
Calculation of Anchor Weighing
Anchor weighing is the process of determining an anchor’s weight in order to calculate potential damage that a ship might cause if it were to become stuck on a reef. Anchor weighing can be done by either measuring the weight of an anchored object or by using a formula. In order to measure the weight of an anchored object, scientists may use a setup called a static balance. This involves suspending a known weight from one end of a spring scale and then measuring how far the other end moves when the suspended weight is tugged on.
Formulas for calculating anchor weighing have been developed over time, but they all share two key features: they take into account both the mass and the drag of an anchor. The mass includes both the anchor itself and any material that surrounds it, such as chains or cables. Drag includes both surface resistance and gravity, so it accounts for not just the weight of an anchor but also its shape and size. Some formulas also include characteristics like depth and wind velocity in order to better estimate how much force will be needed to pull an anchor free.
Conclusion
Congratulations on making it to the end of our article! In this final section, we will be discussing what a ship anchor weighs and how much it would take to break one. Finally, we will give you some advice on things to keep in mind if you find yourself having to remove one from your watery environment. Thanks for reading!